picasso-强大的Android图片下载缓存库
picasso是Square公司开源的一个Android图形缓存库,地址http://square.github.io/picasso/,可以实现图片下载和缓存功能。仅仅只需要一行代码就能完全实现图片的异步加载:
Picasso.with(context).load("http://i.imgur.com/DvpvklR.png").into(imageView);
Api看起来非常独特,是吧。

Picasso不仅实现了图片异步加载的功能,还解决了android中加载图片时需要解决的一些常见问题:
1.在adapter中需要取消已经不在视野范围的ImageView图片资源的加载,否则会导致图片错位,Picasso已经解决了这个问题。
2.使用复杂的图片压缩转换来尽可能的减少内存消耗
3.自带内存和硬盘二级缓存功能
特性以及示例代码:
ADAPTER 中的下载:Adapter的重用会被自动检测到,Picasso会取消上次的加载
@Override public void getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
SquaredImageView view = (SquaredImageView) convertView;
if (view == null) {
view = new SquaredImageView(context);
}
String url = getItem(position);
Picasso.with(context).load(url).into(view);
}
图片转换:转换图片以适应布局大小并减少内存占用
Picasso.with(context)
.load(url)
.resize(50, 50)
.centerCrop()
.into(imageView);
你还可以自定义转换:
public class CropSquareTransformation implements Transformation {
@Override public Bitmap transform(Bitmap source) {
int size = Math.min(source.getWidth(), source.getHeight());
int x = (source.getWidth() - size) / 2;
int y = (source.getHeight() - size) / 2;
Bitmap result = Bitmap.createBitmap(source, x, y, size, size);
if (result != source) {
source.recycle();
}
return result;
}
@Override public String key() { return "square()"; }
}
将CropSquareTransformation 的对象传递给transform 方法即可。
Place holders-空白或者错误占位图片:picasso提供了两种占位图片,未加载完成或者加载发生错误的时需要一张图片作为提示。
Picasso.with(context)
.load(url)
.placeholder(R.drawable.user_placeholder)
.error(R.drawable.user_placeholder_error)
.into(imageView);
如果加载发生错误会重复三次请求,三次都失败才会显示erro Place holder
资源文件的加载:除了加载网络图片picasso还支持加载Resources, assets, files, content providers中的资源文件。
Picasso.with(context).load(R.drawable.landing_screen).into(imageView1);
Picasso.with(context).load(new File(...)).into(imageView2);
下面是picasso源码的解析(不看不影响使用)
Cache,缓存类
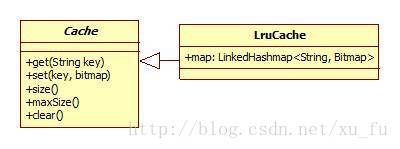
Lrucacha,主要是get和set方法,存储的结构采用了LinkedHashMap,这种map内部实现了lru算法(Least Recently Used 近期最少使用算法)。
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<String, Bitmap>(0, 0.75f, true);
最后一个参数的解释:
true if the ordering should be done based on the last access (from least-recently accessed to most-recently accessed), and false if the ordering should be the order in which the entries were inserted.
因为可能会涉及多线程,所以在存取的时候都会加锁。而且每次set操作后都会判断当前缓存区是否已满,如果满了就清掉最少使用的图形。代码如下
private void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
String key;
Bitmap value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
if (size <= maxSize || map.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
Map.Entry<String, Bitmap> toEvict = map.entrySet().iterator()
.next();
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);
size -= Utils.getBitmapBytes(value);
evictionCount++;
}
}
}
Request,操作封装类

所有对图形的操作都会记录在这里,供之后图形的创建使用,如重新计算大小,旋转角度,也可以自定义变换,只需要实现Transformation,一个bitmap转换的接口。
public interface Transformation {
/**
* Transform the source bitmap into a new bitmap. If you create a new bitmap instance, you must
* call {@link android.graphics.Bitmap#recycle()} on {@code source}. You may return the original
* if no transformation is required.
*/
Bitmap transform(Bitmap source);
/**
* Returns a unique key for the transformation, used for caching purposes. If the transformation
* has parameters (e.g. size, scale factor, etc) then these should be part of the key.
*/
String key();
}
当操作封装好以后,会将Request传到另一个结构中Action。
Action
Action代表了一个具体的加载任务,主要用于图片加载后的结果回调,有两个抽象方法,complete和error,也就是当图片解析为bitmap后用户希望做什么。最简单的就是将bitmap设置给imageview,失败了就将错误通过回调通知到上层。
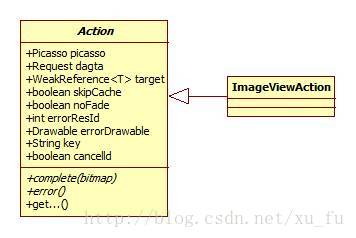
ImageViewAction实现了Action,在complete中将bitmap和imageview组成了一个PicassoDrawable,里面会实现淡出的动画效果。
@Override
public void complete(Bitmap result, Picasso.LoadedFrom from) {
if (result == null) {
throw new AssertionError(String.format(
"Attempted to complete action with no result!\\n%s", this));
}
ImageView target = this.target.get();
if (target == null) {
return;
}
Context context = picasso.context;
boolean debugging = picasso.debugging;
PicassoDrawable.setBitmap(target, context, result, from, noFade,
debugging);
if (callback != null) {
callback.onSuccess();
}
}
有了加载任务,具体的图片下载与解析是在哪里呢?这些都是耗时的操作,应该放在异步线程中进行,就是下面的BitmapHunter。
BitmapHunter
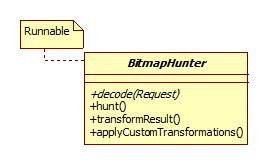
BitmapHunter是一个Runnable,其中有一个decode的抽象方法,用于子类实现不同类型资源的解析。
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.currentThread()
.setName(Utils.THREAD_PREFIX + data.getName());
result = hunt();
if (result == null) {
dispatcher.dispatchFailed(this);
} else {
dispatcher.dispatchComplete(this);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
exception = e;
dispatcher.dispatchRetry(this);
} catch (Exception e) {
exception = e;
dispatcher.dispatchFailed(this);
} finally {
Thread.currentThread().setName(Utils.THREAD_IDLE_NAME);
}
}
abstract Bitmap decode(Request data) throws IOException;
Bitmap hunt() throws IOException {
Bitmap bitmap;
if (!skipMemoryCache) {
bitmap = cache.get(key);
if (bitmap != null) {
stats.dispatchCacheHit();
loadedFrom = MEMORY;
return bitmap;
}
}
bitmap = decode(data);
if (bitmap != null) {
stats.dispatchBitmapDecoded(bitmap);
if (data.needsTransformation() || exifRotation != 0) {
synchronized (DECODE_LOCK) {
if (data.needsMatrixTransform() || exifRotation != 0) {
bitmap = transformResult(data, bitmap, exifRotation);
}
if (data.hasCustomTransformations()) {
bitmap = applyCustomTransformations(
data.transformations, bitmap);
}
}
stats.dispatchBitmapTransformed(bitmap);
}
}
return bitmap;
}
可以看到,在decode生成原始bitmap,之后会做需要的转换transformResult和applyCustomTransformations。最后在将最终的结果传递到上层dispatcher.dispatchComplete(this)。
基本的组成元素有了,那这一切是怎么连接起来运行呢,答案是Dispatcher。
Dispatcher任务调度器
在bitmaphunter成功得到bitmap后,就是通过dispatcher将结果传递出去的,当然让bitmaphunter执行也要通过Dispatcher。

Dispatcher内有一个HandlerThread,所有的请求都会通过这个thread转换,也就是请求也是异步的,这样应该是为了Ui线程更加流畅,同时保证请求的顺序,因为handler的消息队列。
外部调用的是dispatchXXX方法,然后通过handler将请求转换到对应的performXXX方法。
例如生成Action以后就会调用dispather的dispatchSubmit()来请求执行,
void dispatchSubmit(Action action) {
handler.sendMessage(handler.obtainMessage(REQUEST_SUBMIT, action));
}
handler接到消息后转换到performSubmit方法
void performSubmit(Action action) {
BitmapHunter hunter = hunterMap.get(action.getKey());
if (hunter != null) {
hunter.attach(action);
return;
}
if (service.isShutdown()) {
return;
}
hunter = forRequest(context, action.getPicasso(), this, cache, stats,
action, downloader);
hunter.future = service.submit(hunter);
hunterMap.put(action.getKey(), hunter);
}
这里将通过action得到具体的BitmapHunder,然后交给ExecutorService执行。
下面是Picasso.with(context).load("http://i.imgur.com/DvpvklR.png").into(imageView)的过程,
public static Picasso with(Context context) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Builder(context).build();
}
return singleton;
}
public Picasso build() {
Context context = this.context;
if (downloader == null) {
downloader = Utils.createDefaultDownloader(context);
}
if (cache == null) {
cache = new LruCache(context);
}
if (service == null) {
service = new PicassoExecutorService();
}
if (transformer == null) {
transformer = RequestTransformer.IDENTITY;
}
Stats stats = new Stats(cache);
Dispatcher dispatcher = new Dispatcher(context, service, HANDLER,
downloader, cache, stats);
return new Picasso(context, dispatcher, cache, listener,
transformer, stats, debugging);
}
在Picasso.with()的时候会将执行所需的所有必备元素创建出来,如缓存cache、执行executorService、调度dispatch等,在load()时创建Request,在into()中创建action、bitmapHunter,并最终交给dispatcher执行。





