ExtJs4 笔记之 layout 布局
本篇讲解Ext另一个重要的概念:布局。一般的容器类控件都是通过配置项items添加子控件的,这些子控件相对于父控件怎么定位呢,这里就要用到布局。 某些容器类控件,它本身默认就集成了一种布局方式,例如比较典型的是:Ext.container.Viewport 布局控件,它其实就是一个border布局的容器,还有Ext.form.Panel、Ext.tab.Panel等。本节我们系统的分析各种布局方式。
一、absolute
这种方式的布局可以对子元素相对于父级容器控件进行绝对定位,它包含了x、y两个配置项用于定位。
我们来看看一个例子:
//absolute
Ext.create('Ext.Panel', {
title: '容器面板',
renderTo: 'div1',
width: 400,
height: 300,
layout: 'absolute',
items: \[{
title: '面板1',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素1",
width: 200,
height: 100,
x: 50,
y: 50
}, {
title: '面板2',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素2",
width: 200,
height: 100,
x: 100,
y: 80
}\]
});
效果如下:

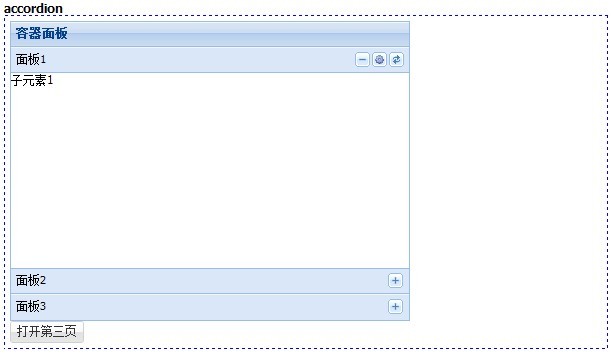
二、accordion
有的js插件里面accordion都是一个ui控件,但是Ext是通过布局的方式实现的,我们可以用面板控件作为它的折叠项,并且还可以用js来翻动活动项。
//accordion
Ext.create('Ext.Panel', {
title: '容器面板',
renderTo: 'div2',
width: 400,
height: 300,
layout: 'accordion',
items: \[{
tools: \[{ type: 'gear', handler: function () {
Ext.Msg.alert('提示', '配置按钮被点击。');
}
}, { type: 'refresh'}\],
title: '面板1',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素1"
}, {
title: '面板2',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素2"
}, {
id: 'panel3',
title: '面板3',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素3"
}\]
});
Ext.create("Ext.Button", {
renderTo: 'div2',
text: "打开第三页",
handler: function () {
Ext.getCmp('panel3').expand(true);
}
});
效果如下:
三、anchor
这个布局就是表单面板默认支持的,每一项占据一行,支持用anchor配置项分配各个子项的高度和宽度。为百分比时表示当前大小占父容器的百分比,为数字的时一般为负数,表示父容器的值减去差值,剩下的为子项的大小。
//anchor
Ext.create('Ext.Panel', {
title: '容器面板',
renderTo: 'div3',
width: 400,
height: 300,
layout: 'anchor',
items: \[{
tools: \[{ type: 'gear', handler: function () {
Ext.Msg.alert('提示', '配置按钮被点击。');
}
}, { type: 'refresh'}\],
title: '面板1',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素1",
anchor: '80% 20%'
}, {
title: '面板2',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素2",
anchor: '-50 -200'
}, {
title: '面板3',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素3",
anchor: '100% 30%'
}\]
});
效果如下:

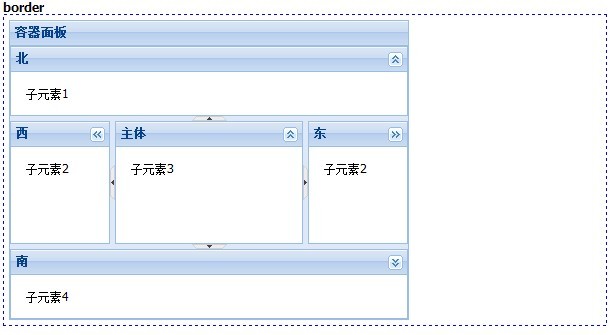
四、border
这个布局可以定义东南西北四个方向的子元素,还有一个居中的子元素,一般用它来做页面整页布局,所以Ext.container.Viewport默认就支持了这个布局方式。
//border
Ext.create('Ext.Panel', {
title: '容器面板',
renderTo: 'div4',
width: 400,
height: 300,
layout: 'border',
defaults: {
split: true, //是否有分割线
collapsible: true, //是否可以折叠
bodyStyle: 'padding:15px'
},
items: \[{
region: 'north', //子元素的方位:north、west、east、center、south
title: '北',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素1",
height: 70
}, {
region: 'west',
title: '西',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素2",
width: 100
}, {
region: 'east',
title: '东',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素2",
width: 100
}, {
region: 'center',
title: '主体',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素3"
}, {
region: 'south',
title: '南',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素4",
height: 70
}\]
});
效果如下:
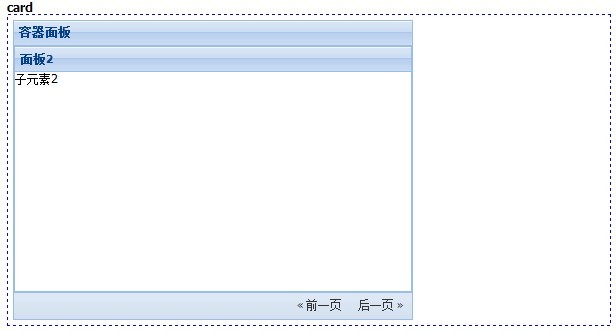
五、card
这个布局可以像卡片一样的切换每个子元素,各个子元素都会独占父元素的容器空间。我们可以定义翻页按钮来控制当前处于活动状态的子元素。
//card
var cardNav = function (incr) {
var l = Ext.getCmp('cardPanel').getLayout();
var i = l.activeItem.id.split('card')\[1\];
var next = parseInt(i, 10) + incr;
l.setActiveItem(next);
Ext.getCmp('cardPrev').setDisabled(next === 0);
Ext.getCmp('cardNext').setDisabled(next === 2);
};
Ext.create('Ext.Panel', {
title: '容器面板',
renderTo: 'div5',
width: 400,
height: 300,
layout: 'card',
activeItem: 1, //默认活动项
id: 'cardPanel',
items: \[{
id: 'card0',
title: '面板1',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素1"
}, {
id: 'card1',
title: '面板2',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素2"
}, {
id: 'card2',
title: '面板3',
xtype: "panel",
html: "子元素3"
}\],
bbar: \['->', {
id: 'cardPrev',
text: '« 前一页',
handler: Ext.Function.bind(cardNav, this, \[-1\])
}, {
id: 'cardNext',
text: '后一页 »',
handler: Ext.Function.bind(cardNav, this, \[1\])
}\]
});
效果如下:
六、column
这个布局把子元素按照列进行划分。
//column
Ext.create('Ext.Panel', {
title: '容器面板',
renderTo: 'div6',
width: 400,
height: 300,
layout: 'column',
defaults: { //设置没一列的子元素的默认配置
layout: 'anchor',
defaults: {
anchor: '100%'
}
},
items: \[{
columnWidth: 4 / 10, //设置列的宽度
items: \[{
title: '面板1',
border: false,
html: '子元素1'
}, {
title: '面板2',
border: false,
html: '子元素2'
}\]
}, {
width: 120,
items: \[{
title: '面板3',
border: false,
html: '子元素3'
}\]
}, {
columnWidth: .40,
items: \[{
title: '面板4',
border: false,
html: '子元素4'
}\]
}\]
});
效果如下:

七、fit
这个布局下子元素会独占全部的容器空间,一般用于只有一个子项的情况。
//fit
Ext.create('Ext.Panel', {
title: '容器面板',
renderTo: 'div7',
width: 400,
height: 300,
layout: 'fit',
items: \[{
title: '面板',
html: '子元素',
border: false
}\]
});
效果如下:

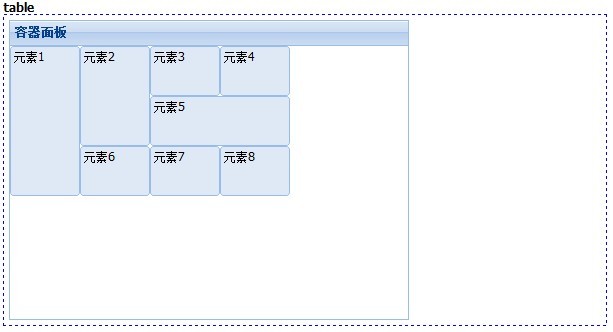
八、table
这个布局用表格定位的方式去组织子元素,我们可以像表格一样设置rowspan和colspan。
//table
Ext.create('Ext.Panel', {
title: '容器面板',
renderTo: 'div8',
width: 400,
height: 300,
layout: {
type: 'table',
columns: 4
},
defaults: { frame: true, width: 70, height: 50 },
items: \[
{ html: '元素1', rowspan: 3, height: 150 },
{ html: '元素2', rowspan: 2, height: 100 },
{ html: '元素3' },
{ html: '元素4' },
{ html: '元素5', colspan: 2, width: 140 },
{ html: '元素6' },
{ html: '元素7' },
{ html: '元素8' }
\]
});
效果如下:
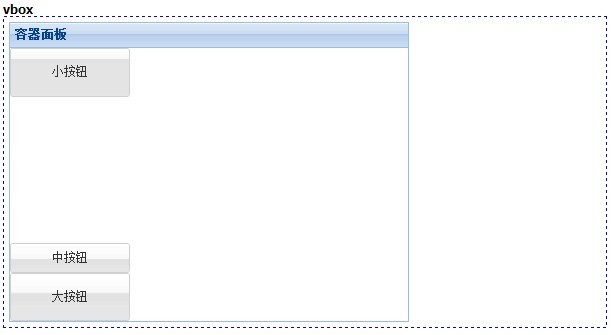
九、vbox
这个布局把所有的子元素按照纵向排成一列。
//vbox
Ext.create('Ext.Panel', {
title: '容器面板',
renderTo: 'div9',
width: 400,
height: 300,
layout: {
type: 'vbox',
pack: 'start', //纵向对齐方式 start:从顶部;center:从中部;end:从底部
align: 'stretchmax' //对齐方式 center、left、right:居中、左对齐、右对齐;stretch:延伸;stretchmax:以最大的元素为标准延伸
},
defaults: {
xtype: 'button'
},
items: \[{
text: '小按钮',
flex: 1 //表示当前子元素尺寸所占的均分的份数。
}, {
xtype: 'tbspacer', //插入的空填充
flex: 3
},
{
text: '中按钮',
scale: 'medium'
}, {
text: '大按钮',
width: 120,
scale: 'large',
flex: 1
}\]
});
效果如下:
十、hbox
跟vbox类似,只不过变成了横向的。
//hbox
Ext.create('Ext.Panel', {
title: '容器面板',
renderTo: 'div10',
width: 400,
height: 300,
layout: {
type: 'hbox',
pack: 'end',
align: 'middle' //对齐方式 top、middle、bottom:顶对齐、居中、底对齐;stretch:延伸;stretchmax:以最大的元素为标准延伸
},
defaults: {
xtype: 'button'
},
items: \[{
text: '小按钮'
},{
text: '中按钮',
scale: 'medium'
}, {
text: '大按钮',
width: 120,
scale: 'large'
}\]
});
效果如下:






